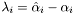 and there are
and there are 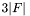 variables, where
variables, where 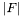 is the number of triangles in the mesh. The quadratic objective is to minimize
is the number of triangles in the mesh. The quadratic objective is to minimize 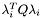 , where Q is just an identity matrix, and variables are subject to the following 4 types of constraints:
, where Q is just an identity matrix, and variables are subject to the following 4 types of constraints:#include <AnglesOptimization.h>
The variable of the quadratic program are 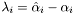 and there are
and there are 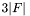 variables, where
variables, where 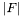 is the number of triangles in the mesh. The quadratic objective is to minimize
is the number of triangles in the mesh. The quadratic objective is to minimize 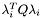 , where Q is just an identity matrix, and variables are subject to the following 4 types of constraints:
, where Q is just an identity matrix, and variables are subject to the following 4 types of constraints:
1. 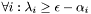 Where we picked
Where we picked 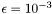 to ensure that ">" relation is satisfied.
to ensure that ">" relation is satisfied.
2. 
The sum of the current 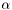 s in each triangle is subtracted from
s in each triangle is subtracted from 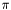 to ensure that
to ensure that 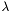 s sum to the correct value, a similar subtraction is done in the next two matrices.
s sum to the correct value, a similar subtraction is done in the next two matrices.
3.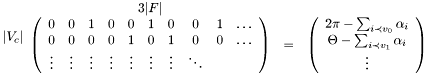
In the standard case, the sum of the angles around any internal vertex is fixed to 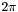 and the sum of the angles around any boundary vertex is left free. However one can also fix boundary angles to control the shape of the parameter domain. It is also possible to fix the sum of the angles around some internal vertices to
and the sum of the angles around any boundary vertex is left free. However one can also fix boundary angles to control the shape of the parameter domain. It is also possible to fix the sum of the angles around some internal vertices to 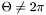 , which makes this vertices cone singularities, while the rest of the parameterization remains continuous piecewise flat surface. In this case
, which makes this vertices cone singularities, while the rest of the parameterization remains continuous piecewise flat surface. In this case 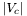 is the number of vertices, for which the cone angle is fixed (it is also possible to fix the range of the sum).
is the number of vertices, for which the cone angle is fixed (it is also possible to fix the range of the sum).
4. 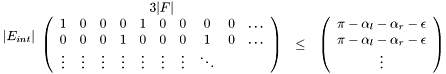
Where 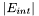 is the number of internal edges, because the previous constraints ensure that
is the number of internal edges, because the previous constraints ensure that 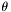 for the boundary edge are within the valid bounds. The {0,1} values in all the above matrices correspond to incidence relations is described in the following figure.
for the boundary edge are within the valid bounds. The {0,1} values in all the above matrices correspond to incidence relations is described in the following figure.
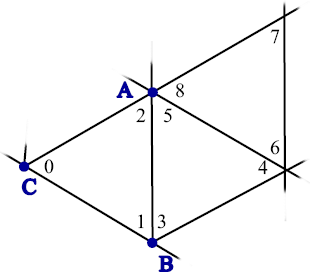
Definition at line 99 of file AnglesOptimization.h.
Public Member Functions | |
| AnglesOptimization (Mesh *_mesh, const MSKenv_t &env) | |
| Creates angle optimization task. | |
| void | doSolve () |
| Call this function after the object is created to perform the optimization. | |
| void | setDataStructres () |
| Sets linear constraints and quadratic objective. | |
| void | optimize () |
| Calls MOSEK functions to optimize the task and save the solution. | |
| void | allocateMosekArrays () |
| Alocates arrays and matrices required by Mosek. | |
| void | clearMosekArrays () |
| Deletes arrays and matrices required by Mosek. | |
| ~AnglesOptimization (void) | |
| Clears mosek task. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const double | epsRange = 1.0e-3 |
| Value of epsilon: how far can the values of alphas be from 0 or PI. | |
Private Attributes | |
| Mesh * | mesh |
| MSKtask_t | task |
| int | NUMCON |
| Number of constraints. | |
| int | NUMVAR |
| Number of variables. | |
| int | NUMANZ |
| Number of nonzeros in A (constraint matrix). | |
| int | NUMQNZ |
| Number of nonzeros in Q (quadratic objective matrix). | |
| int * | bkc |
| Type of the constraint. | |
| double * | blc |
| Lower bound on the constraint. | |
| double * | buc |
| Upper bound on the constraint. | |
| int * | ptrb |
| For representation of sparse constraint matrix: beginning of the row. | |
| int * | ptre |
| For representation of sparse constraint matrix: ending of the row. | |
| int * | sub |
| For representation of sparse constraint matrix: subscripts for nonzero values in the row. | |
| double * | val |
| For representation of sparse constraint matrix: values in the matrix. | |
| int * | bkx |
| Type of the constraint on the variable. | |
| double * | blx |
| Lower bound on the variable. | |
| double * | bux |
| Upper bound on the variable. | |
| double * | c |
| Linear minimization part. | |
| int * | qsubi |
| Quadratic objective matrix j subscript. | |
| int * | qsubj |
| Quadratic objective matrix i subscript. | |
| double * | qval |
| Quadratic objective matrix non-zero values. | |
| double * | xx |
| Variable that we optimize for - alpha angles. | |
|
||||||||||||
|
Creates angle optimization task. Computes number of variables, constraints, number of non-zeros in constraint and objective matrix. Definition at line 17 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00017 { 00018 mesh = _mesh; 00019 00020 NUMVAR = mesh->numFaces() * 3; 00021 NUMCON = mesh->numFaces() + mesh->numVertices() + mesh->numEdges() - mesh->numBoundary(); 00022 NUMANZ = 3*NUMVAR - mesh->numBoundary(); 00023 NUMQNZ = NUMVAR; 00024 00026 int r = MSK_RES_OK; 00027 r = MSK_maketask(env, NUMCON, NUMVAR, &task); 00028 check_error (r != MSK_RES_OK, "Cannot make MOSEK task for angle optimization."); 00029 r = MSK_linkfiletotaskstream(task, MSK_STREAM_LOG, "_AngleOptMosekOut.txt", 0); 00030 check_error (r != MSK_RES_OK, "Cannot link MOSEK \"_AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" output file."); 00031 }
|
|
|
Clears mosek task.
Definition at line 237 of file AnglesOptimization.h. 00237 { clearMosekArrays(); }
|
|
|
Alocates arrays and matrices required by Mosek.
Definition at line 259 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00259 { 00260 bkc = new int[NUMCON]; bkx = new int[NUMVAR]; 00261 ptrb = new int[NUMVAR]; ptre = new int[NUMVAR]; 00262 sub = new int[NUMANZ]; 00263 qsubi = new int[NUMQNZ]; qsubj = new int[NUMQNZ]; 00264 00265 blc = new double[NUMCON]; buc = new double[NUMCON]; 00266 c = new double[NUMVAR]; blx = new double[NUMVAR]; 00267 bux = new double[NUMVAR]; val = new double[NUMANZ]; 00268 xx = new double[NUMVAR]; qval = new double[NUMQNZ]; 00269 }
|
|
|
Deletes arrays and matrices required by Mosek.
Definition at line 271 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00271 { 00272 00273 if (task) { 00274 delete [] bkc; delete [] bkx; delete [] ptrb; 00275 delete [] ptre; delete [] sub; delete [] qsubi; delete [] qsubj; 00276 delete [] buc; delete [] c; delete [] blx; delete [] blc; 00277 delete [] bux; delete [] val; delete [] xx; delete [] qval; 00278 MSK_deletetask(&task); 00279 task = NULL; 00280 } 00281 }
|
|
|
Call this function after the object is created to perform the optimization. The function allocates arrays for mosek datastructure, computes initial angles and sets datastructures for optimization. Than optimization function is called. Definition at line 39 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00039 { 00040 allocateMosekArrays(); 00041 setDataStructres(); 00042 optimize(); 00043 }
|
|
|
Calls MOSEK functions to optimize the task and save the solution. Input the lower triangular part of the Q for the objective. (Our weight matrix) Perform optimization Output solution summary Get solution from MOSEK Save solution of the optimization (alpha angles). Compute valid theta angles. Definition at line 182 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00182 { 00183 int r = MSK_RES_OK; 00184 r = MSK_inputdata(task, NUMCON,NUMVAR, NUMCON,NUMVAR, c, 00185 0.0, ptrb, ptre, sub, val, bkc, blc, buc, bkx, blx, bux); 00186 00187 check_error ( r != MSK_RES_OK, 00188 "Could not input constraints for angle optimization.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00189 00191 int count = 0; 00192 for (count = 0; count < NUMVAR; count++) { 00193 qsubi[count] = count; 00194 qsubj[count] = count; 00195 qval[count] = 1; 00196 } 00197 00198 r = MSK_putqobj(task, NUMQNZ, qsubi, qsubj, qval); 00199 check_error ( r != MSK_RES_OK, 00200 "Could not input objective for angle optimization.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00201 00202 00204 r = MSK_optimize(task); 00205 check_error ( r != MSK_RES_OK, 00206 "Could not solve angle optimization. Possibly the problem is infisible.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00207 00209 r = MSK_solutionsummary(task, MSK_STREAM_ERR); 00210 check_error ( r != MSK_RES_OK, 00211 "Could not output solution summary.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00212 00213 //MSK_writedata(task,"problem.mbt"); 00215 int ps, ss; 00216 r = MSK_getsolution (task, MSK_SOL_ITR, &ps, &ss, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, xx, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL); 00217 00218 check_error ( r != MSK_RES_OK, "Could not get solution of angle optimization.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00219 check_error ( ps != MSK_PRO_STA_PRIM_AND_DUAL_FEAS, 00220 "Either problem is infisible or could not find optimal solution for some other reason.\n Check \"AngleOptMosekOut.txt\" for output." ); 00221 00223 Mesh::HalfEdgeIterator hIter = mesh->halfEdgeIterator(); 00224 count = 0; 00225 for (hIter.reset(); !hIter.end(); hIter++) { 00226 Edge * e = hIter.half_edge(); 00227 if (e->face) 00228 e->alphaOposite = e->alphaOposite + xx[count++]; 00229 else 00230 e->alphaOposite = 0; 00231 } 00232 00233 00235 Mesh::EdgeIterator eIter = mesh->edgeIterator(); 00236 for (eIter.reset(); !eIter.end(); eIter++){ 00237 Edge * e = eIter.edge(); 00238 e->setTheta (M_PI - e->alphaOposite - e->pair->alphaOposite); 00239 e->pair->setTheta (e->theta()); 00240 } 00241 00242 Mesh::VertexIterator vIter = mesh->vertexIterator(); 00243 for (vIter.reset(); !vIter.end(); vIter++) { 00244 vIter.vertex()->cone_angle = 0; 00245 } 00246 00247 for (eIter.reset(); !eIter.end(); eIter++) { 00248 Edge * e = eIter.edge(); 00249 e->vertex->cone_angle += e->theta(); 00250 e->pair->vertex->cone_angle += e->theta(); 00251 } 00252 00253 for (vIter.reset(); !vIter.end(); vIter++) { 00254 vIter.vertex()->cone_angle /= M_PI; 00255 } 00256 }
|
|
|
Sets linear constraints and quadratic objective. Define bounds for the constraint. Sum of angles in each face is M_PI Sum of angles around each internal non-singularity vertex is 2*M_PI Sum of angles around singularity or constrained boundary vertex is v.cone_angle*M_PI Sum of angles around unconstrained boundary vertex is free Sum of angles oposite to internal edge should be less then M_PI Define information for the variables. Definition at line 45 of file AnglesOptimization.cpp. 00045 { 00046 00048 int k = 0; 00049 int kBefore = 0; 00050 00052 Mesh::FaceIterator fIter = mesh->faceIterator(); 00053 for ( ; !fIter.end(); fIter++) { 00054 k = fIter.face()->ID; 00055 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_FX; 00056 blc[k] = M_PI; 00057 buc[k] = M_PI; 00058 } 00059 00060 kBefore = mesh->numFaces(); 00061 00065 Mesh::VertexIterator vIter = mesh->vertexIterator(); 00066 for (; !vIter.end(); vIter++) { 00067 Vertex * v = vIter.vertex(); 00068 k = kBefore + v->ID; 00069 00070 if (!v->constrained) { 00071 if (!v->isBoundary()) { 00072 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_FX; 00073 blc[k] = 2*M_PI; 00074 buc[k] = 2*M_PI; 00075 } 00076 else { 00077 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_RA; 00078 blc[k] = 0; 00079 buc[k] = 2*M_PI; 00080 } 00081 } 00082 else { 00083 if (v->max_cone_angle == v->min_cone_angle) 00084 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_FX; 00085 else 00086 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_RA; 00087 blc[k] = v->min_cone_angle*M_PI; 00088 buc[k] = v->max_cone_angle*M_PI; 00089 } 00090 } 00091 00092 kBefore += mesh->numVertices(); 00093 k = kBefore; 00094 00096 Mesh::EdgeIterator eIter = mesh->edgeIterator(); 00097 for ( ; !eIter.end(); eIter++) { 00098 Edge * e = eIter.edge(); 00099 if (!e->isBoundary()) { 00100 e->ID = k; 00101 e->pair->ID = e->ID; 00102 00103 bkc[k] = MSK_BK_RA; 00104 blc[k] = epsRange; 00105 buc[k] = M_PI - epsRange; 00106 k++; 00107 } 00108 } 00109 00110 /* Because we solve for difference between initial angles and valid angles , */ 00111 /* we need to subtruct initial angles from sum conditions. */ 00112 Mesh::HalfEdgeIterator hIter = mesh->halfEdgeIterator(); 00113 for (; !hIter.end(); hIter++) { 00114 Edge * e = hIter.half_edge(); 00115 if (e->face) { 00116 int vId = e->oppositeVertex()->ID; 00117 int fId = e->face->ID; 00118 int eId = e->ID; 00119 00120 vId += mesh->numFaces(); 00121 00122 blc[fId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00123 buc[fId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00124 blc[vId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00125 buc[vId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00126 00127 if (!e->isBoundary()) { 00128 blc[eId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00129 buc[eId] -= e->alphaOposite; 00130 } 00131 } 00132 } 00133 00134 00136 int currPtr = 0; 00137 int count = 0; 00138 00139 for (hIter.reset(); !hIter.end(); hIter++) { 00140 Edge * e = hIter.half_edge(); 00141 if (e->face) { 00142 Edge * e = hIter.half_edge(); 00143 00144 /* Linear minim part*/ 00145 c[count] = 0.0; 00146 00147 /* Constraint matrix (our A). */ // assigning over the columns 00148 ptrb[count] = currPtr; 00149 00150 if (e->isBoundary()) 00151 ptre[count] = currPtr + 2; 00152 else 00153 ptre[count] = currPtr + 3; 00154 00155 int fId = e->face->ID; 00156 sub[currPtr] = fId; 00157 val[currPtr] = 1.0; 00158 currPtr++; 00159 00160 int vId = e->oppositeVertex()->ID; 00161 vId += mesh->numFaces(); 00162 sub[currPtr] = vId; 00163 val[currPtr] = 1.0; 00164 currPtr++; 00165 00166 if (!e->isBoundary()) { 00167 int eId = e->ID; 00168 sub[currPtr] = eId; 00169 val[currPtr] = 1.0; 00170 currPtr++; 00171 } 00172 00173 /* Bounds. */ 00174 bkx[count] = MSK_BK_RA; 00175 blx[count] = epsRange - e->alphaOposite; 00176 bux[count] = (M_PI - epsRange) - e->alphaOposite; 00177 count++; 00178 } 00179 } 00180 }
|
|
|
Type of the constraint. Size: NUMCON Definition at line 120 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Type of the constraint on the variable. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 163 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Lower bound on the constraint. Size: NUMCON Definition at line 126 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Lower bound on the variable. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 169 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Upper bound on the constraint. Size: NUMCON Definition at line 132 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Upper bound on the variable. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 175 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Linear minimization part. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 182 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Value of epsilon: how far can the values of alphas be from 0 or PI.
Definition at line 213 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 103 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Number of nonzeros in A (constraint matrix).
Definition at line 112 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Number of constraints.
Definition at line 108 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Number of nonzeros in Q (quadratic objective matrix).
Definition at line 114 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Number of variables.
Definition at line 110 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
For representation of sparse constraint matrix: beginning of the row. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 138 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
For representation of sparse constraint matrix: ending of the row. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 144 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Quadratic objective matrix j subscript. Size: NUMQNZ Definition at line 188 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Quadratic objective matrix i subscript. Size: NUMQNZ Definition at line 194 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Quadratic objective matrix non-zero values. The lower triangular part. Size: NUMQNZ Definition at line 201 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
For representation of sparse constraint matrix: subscripts for nonzero values in the row. Size: NUMANZ Definition at line 150 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Definition at line 105 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
For representation of sparse constraint matrix: values in the matrix. Size: NUMANZ Definition at line 156 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
|
|
Variable that we optimize for - alpha angles. Size: NUMVAR Definition at line 208 of file AnglesOptimization.h. |
 1.4.5
1.4.5